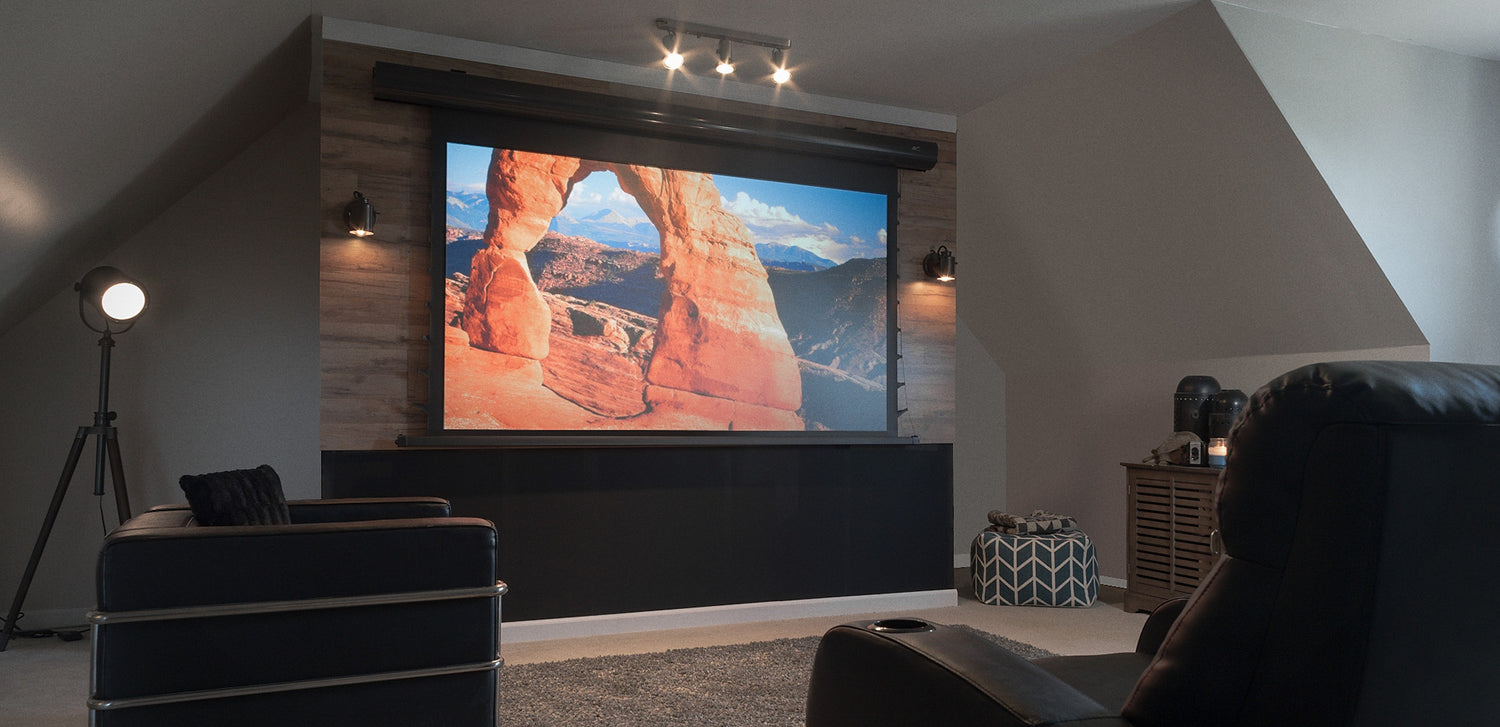
Different Types of Screens
-
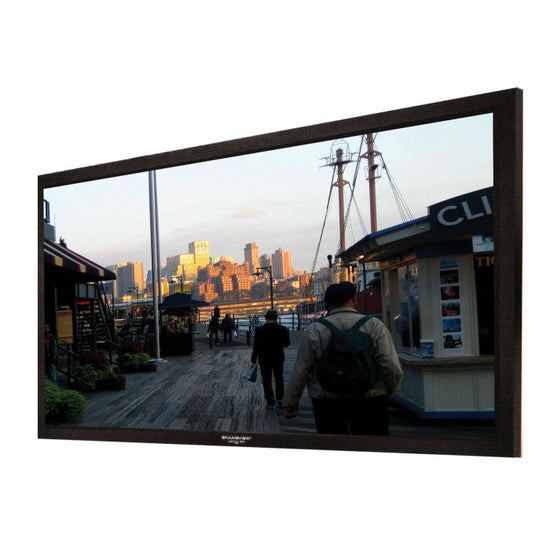

Fixed Screens
These screens are mounted in a permanent frame and are typically used in home theaters and small conference rooms. Fixed frame screens are available in a variety of sizes and aspect ratios, and can be made from a variety of materials such as vinyl, fabric, or tensioned materials.
-

Manual Pull Down Screens
These screens are mounted on a roll and can be manually pulled down when needed. They are typically used in small conference rooms and classrooms, and can be made from a variety of materials such as vinyl or fabric.
-
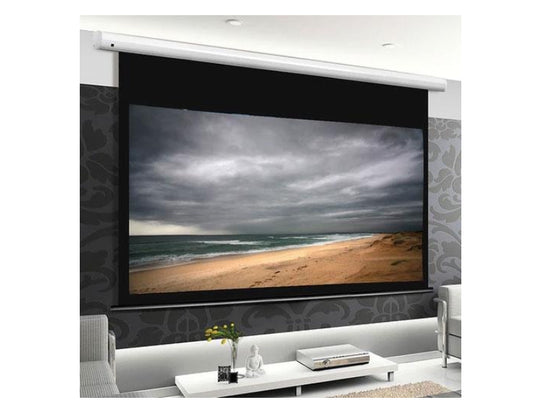

Motorized Screens
These screens can be raised and lowered using a motor with a remote control, and are typically used in large conference rooms and home theaters. Motorized screens are available in a variety of sizes and aspect ratios, and can be made from a variety of materials such as vinyl or fabric.
-

Curved Screens
These types of screens have a curved shape, this is to enhance the image, and make the viewer experience more immersive. The curvature of the screen creates a more uniform image and a wider field of view, making the image appear more natural and lifelike. One of the main advantages of curved screens is that they reduce the distortion that can occur at the edges of a flat screen. The edges of the screen are pulled inwards, which means that the edges of the image appear more natural, and the center of the screen is not distorted.
-
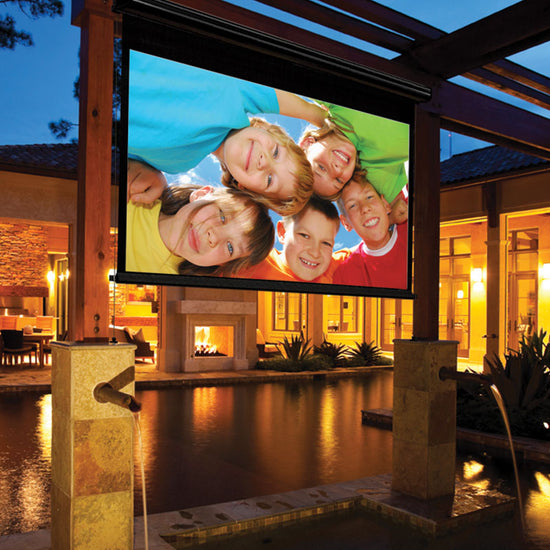

Outdoor Screens
These screens are designed to be used outdoors and are made from materials that can withstand the elements. They typically have a higher gain and a wider viewing angle to accommodate for ambient lighting.
-
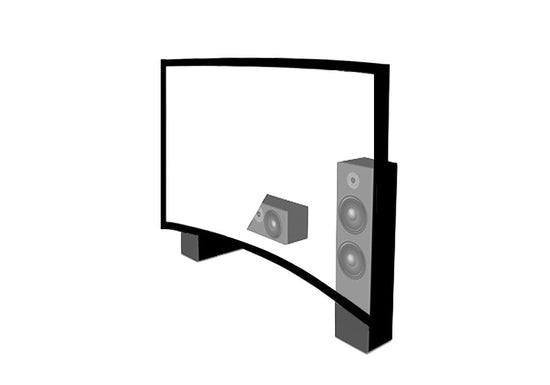
Accoustic Screens
Acoustic screens are projector screens specifically designed to improve the audio experience in a room. They are often used in spaces such as home theaters, conference rooms, and performance venues. These screens typically feature a perforated surface that allows sound to pass through, but with a dampening effect. They may also be designed to help control the direction of sound, directing it towards the audience rather than reflecting it back towards the projector.







